Process to manufacture an industrial sewing machine to the point of completion
We adopt integrated production ranging from processing, painting, and assembly to packing and shipping.
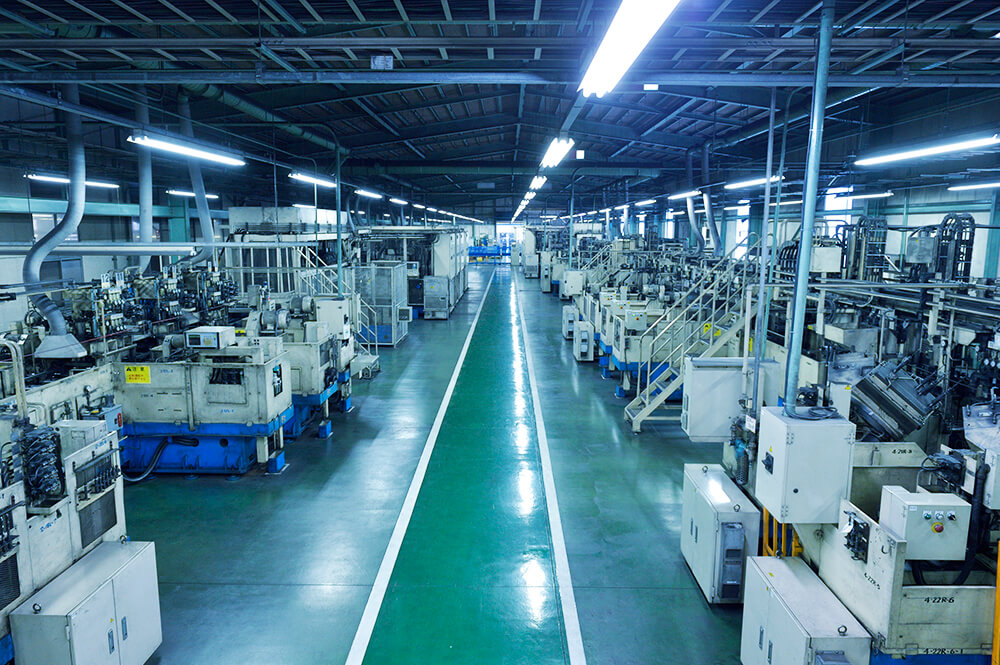
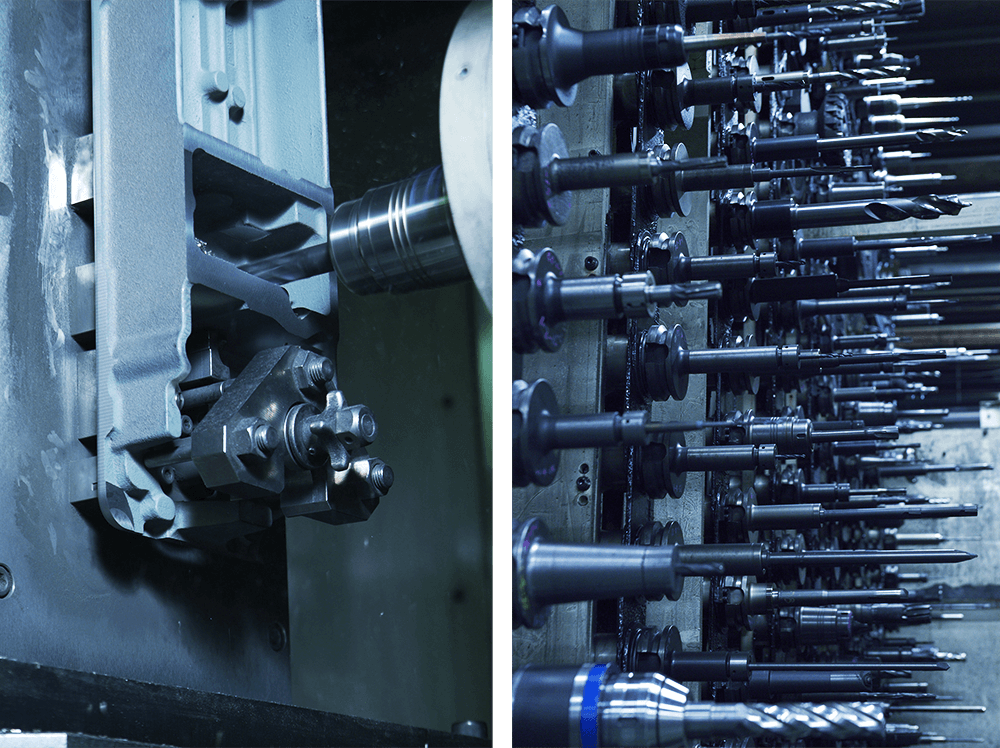
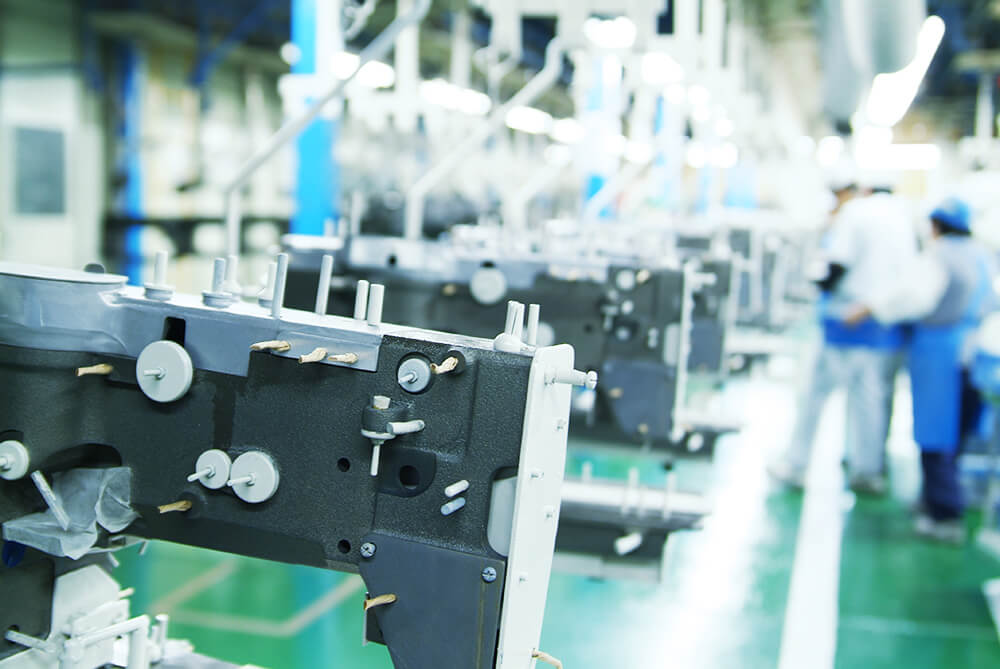
Frame machining
This process surface cuts the frame (an arm and a bed) that serves as the core of an industrial sewing machine and then machines the screw holes, all with high accuracy and speed through computer control using a machining center (a numerically controlled-machine tool). Original JUKI tools designed in the most suitable shape are finely applied to this cutting and machining process for various kinds and various volumes production.
Machining center
Many of the processing machines (machining centers) lined up on the production line perform machining operations non-stop 24 hours a day.

Frame machining
This machining takes place while large numbers of cutting tools such as a superparticulate tool are exchanged automatically using a program adapted to the sewing machine type.
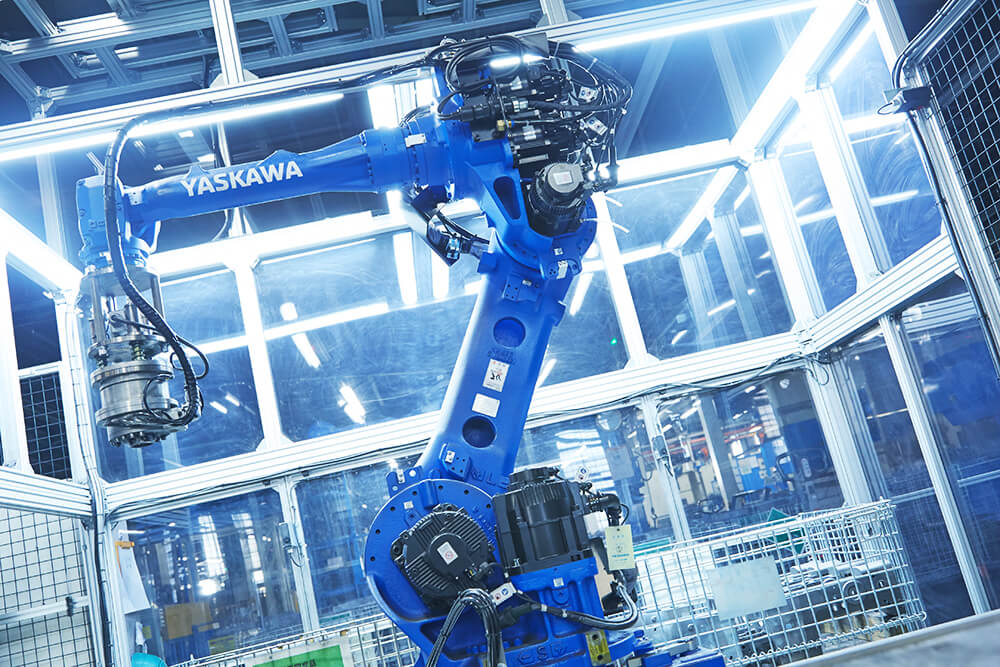
Transportation by a materialhandling robot
The fully machined frame is transported on a palette, inspected by a 3D camera, and picked up and transported again by a material-handling robot.

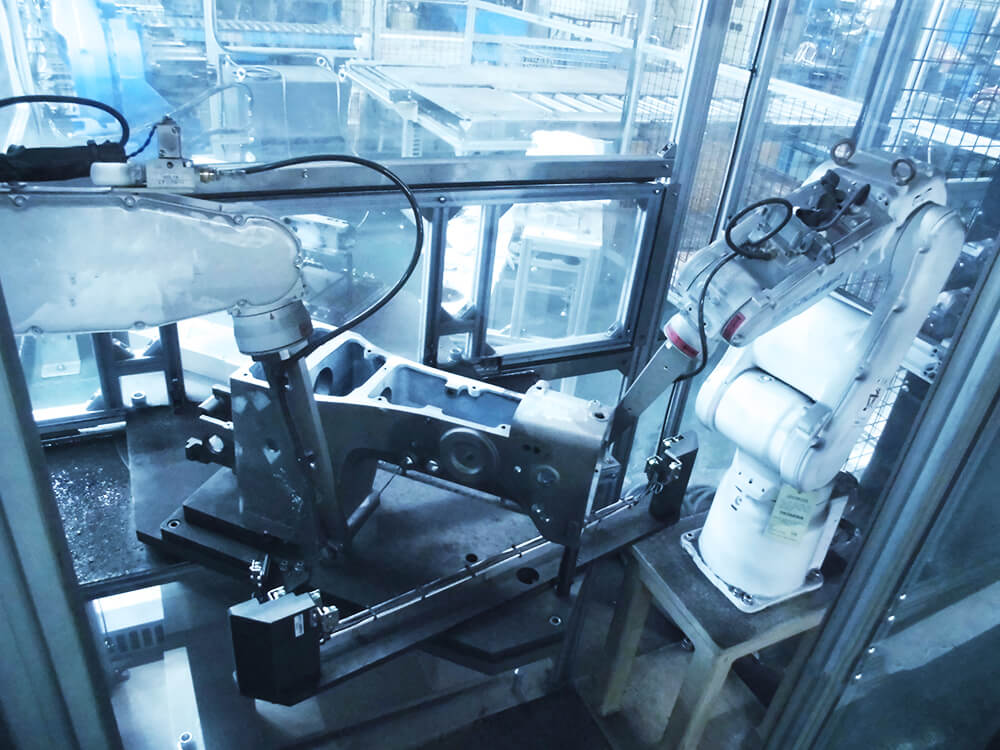
Removal of the residual chips and shavings by the air-blowing robots
Two robots blow air to remove the chips and shavings left in screw holes and on surfaces after machining.

Painting
The machined frame is covered with a powder coating. The robot powder-coats the body automatically using a program adapted to the sewing machine type to improve workability and safety and avoid adverse paint and chemical exposure to the human body. No longer does a skillful person in charge handle the painting of special sewing machines. Everything is robotized. The coating performance and coating efficiency of the paint are now raised by heating the frame before applying the undercoat.
Masking
The machine is masked before the painting to block parts with screwholes that are not to be painted.

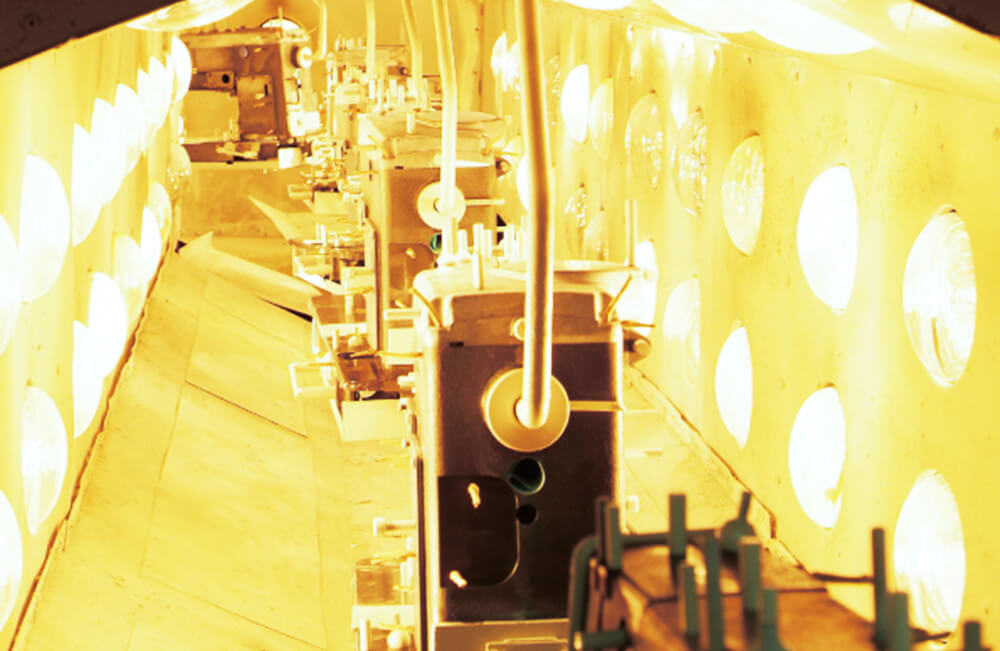
Pre-heat
The frame is heated before applying the undercoat to raise the coating efficiency of the paint.

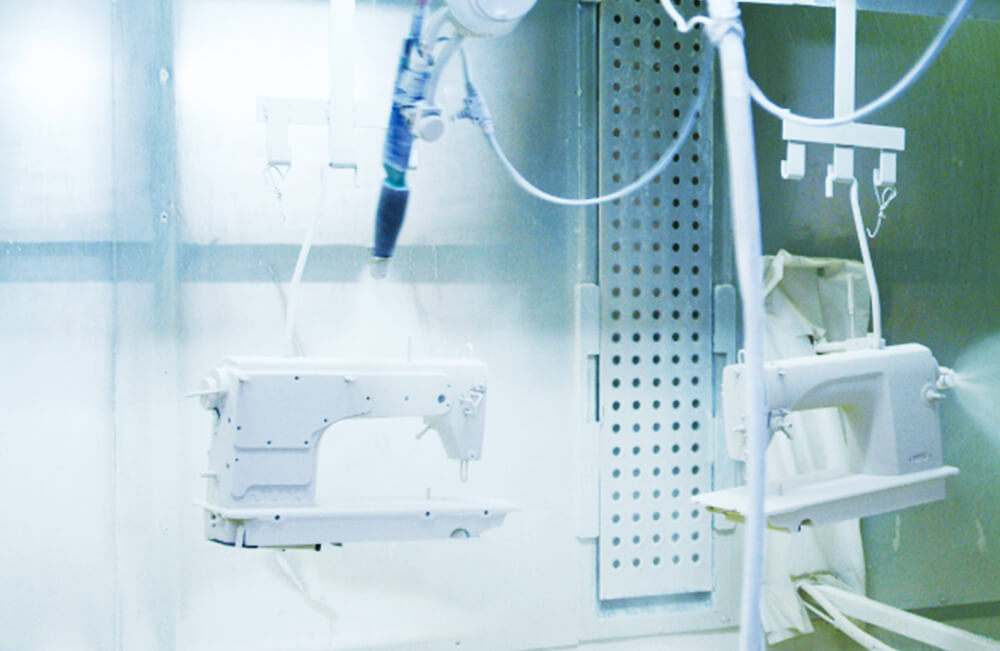
Painting by robot
The direction of application is adjusted to suit the sewing machine type in order to paint the machine with the most efficient program procedure. The overcoating process, undercoating process, and manual painting have all been robotized.

Printing of a JUKI logo
After painting by robot, this process performs print dryness and prints a “JUKI” logo. This process runs manually, under the concept of “careful handling, one by one.”
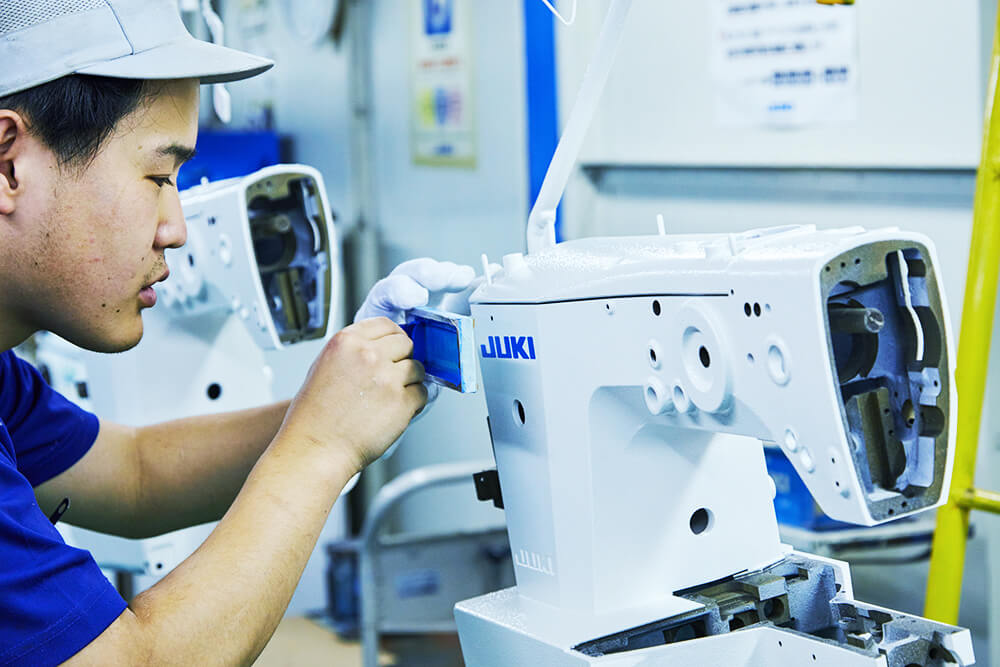

Assembly
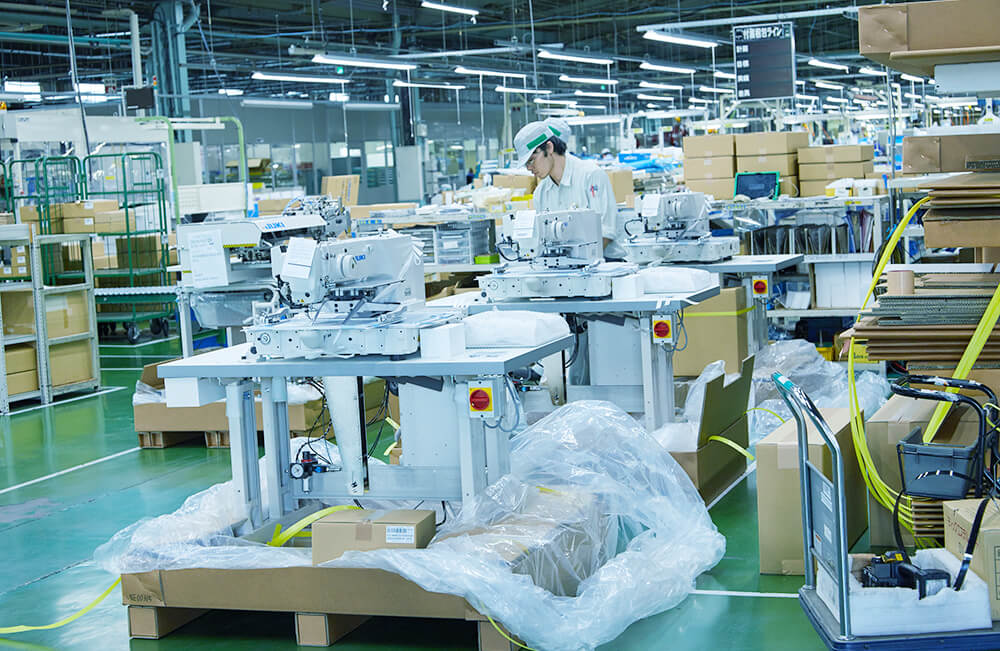
In this process, workers mount parts, driving motors, thread trimming units, etc. on painted frames according to an assembly procedure and a “digital cell production” system that displays necessary parts and tools on the monitor screen.
Every cell has been built by in-house development. The system easily prevents erroneous assembly, reduces work-learning times, and easily accommodates various kinds and various volumes production. We improve the skill of employees through an original screening system.
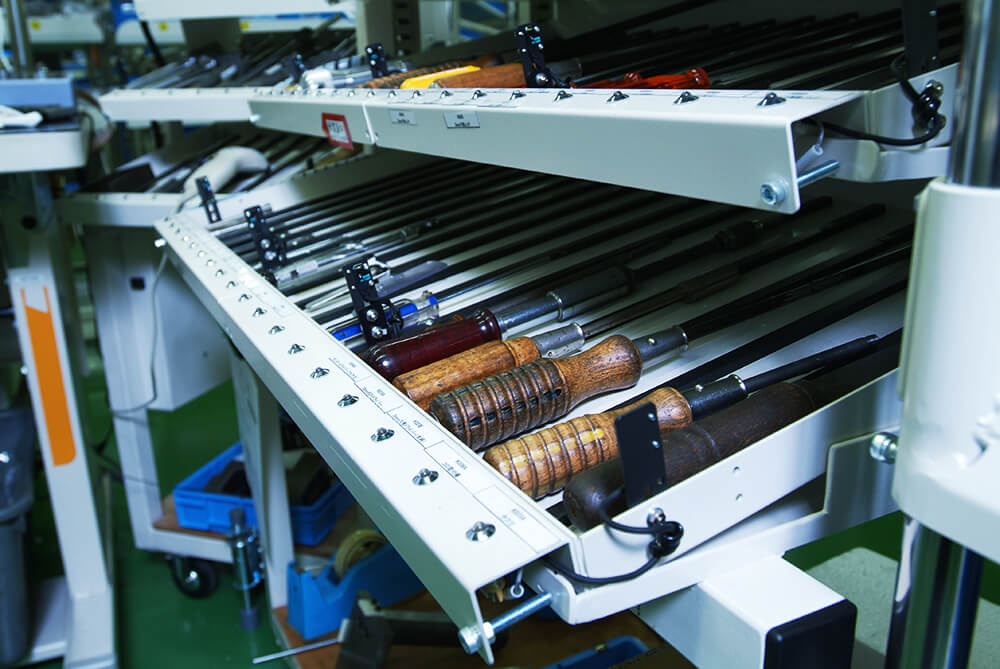

Tools for assembly
In an assembly process, the management of the tools used, assembled parts, screw tightening torques, etc. is unified by computers linked to a central server.
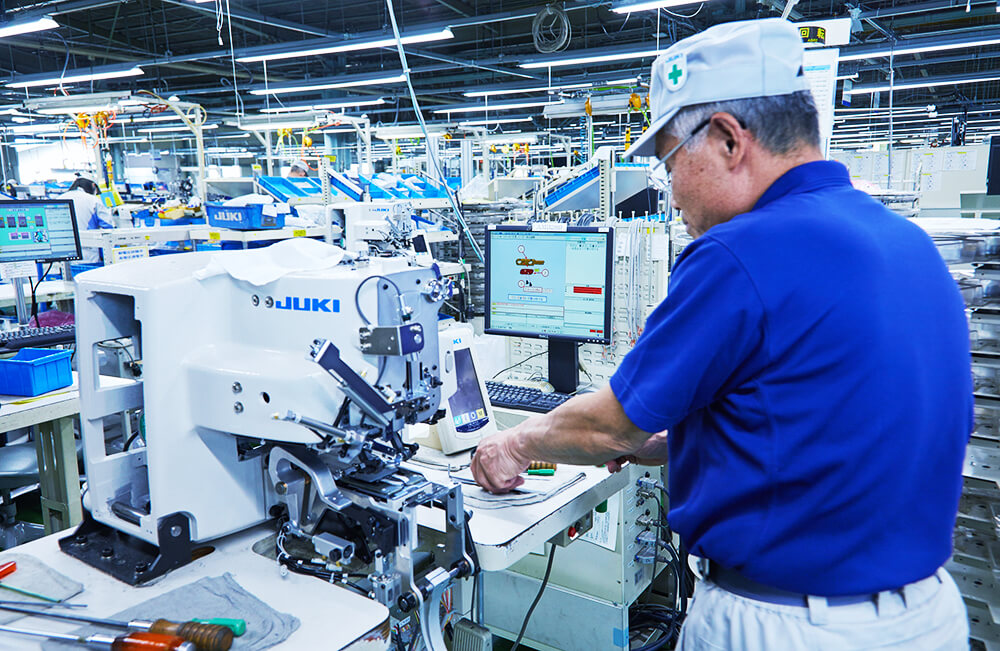

Digital cell production using “a self-contained system”
It began in 2004. A worker using this system can complete a product even when handling a long or complicated assembly process alone. All steps in the assembly process are clearly displayed on the monitor. (For production of a special sewing machine and an automatic machine)
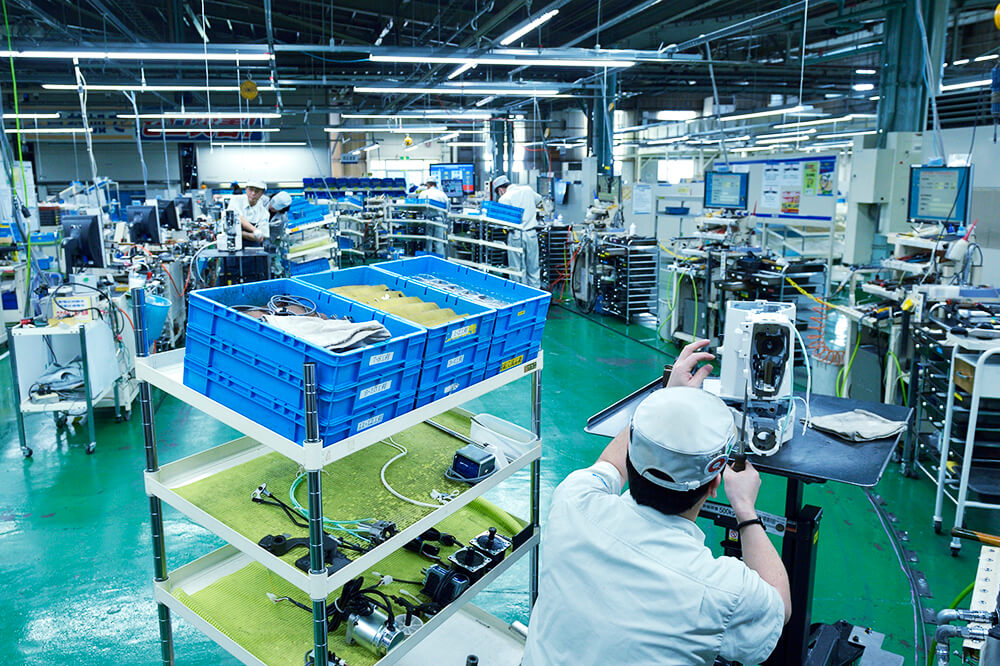

Digital cell production using “a mixed flow system”
It began in 2016. A worker using this system divides a process for assembling several types of sewing machines and assembles the different types of sewing machines alternately on a mobile work table. (Mainly, for high-mix low-volume production)
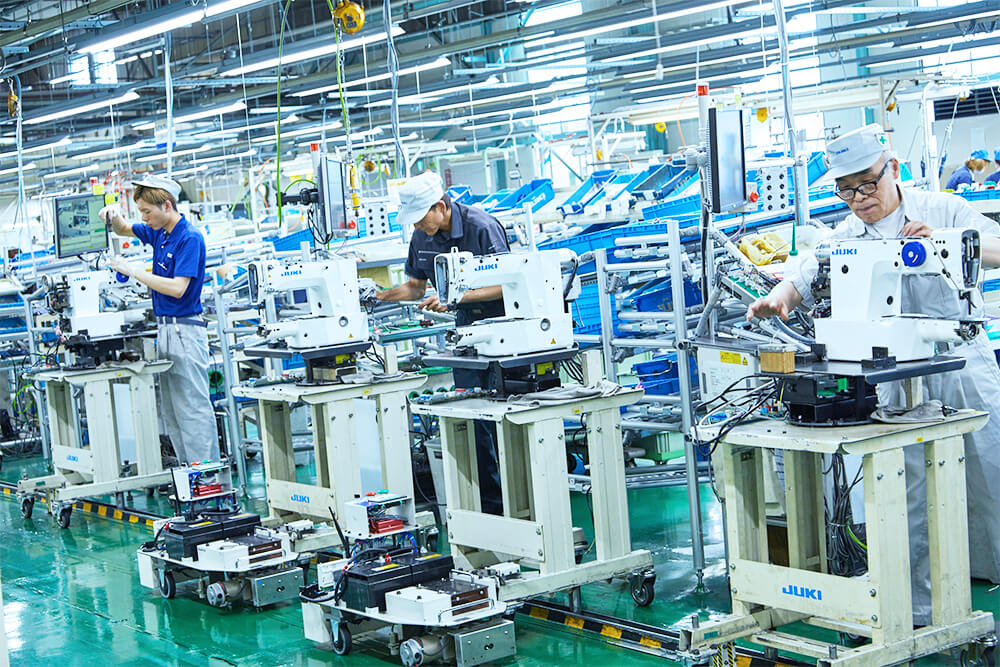

Digital cell production supported by “a takt system using AGVs (Automated Guided Vehicles)”
This production system, introduced in 2018, is now being used mostly to assemble “products for mass production.” The system enables AGVs to move on to the next process at a specified takt time, allowing the person in charge of the next process to complete the predetermined assembly in synch with the takt time.
Product completion
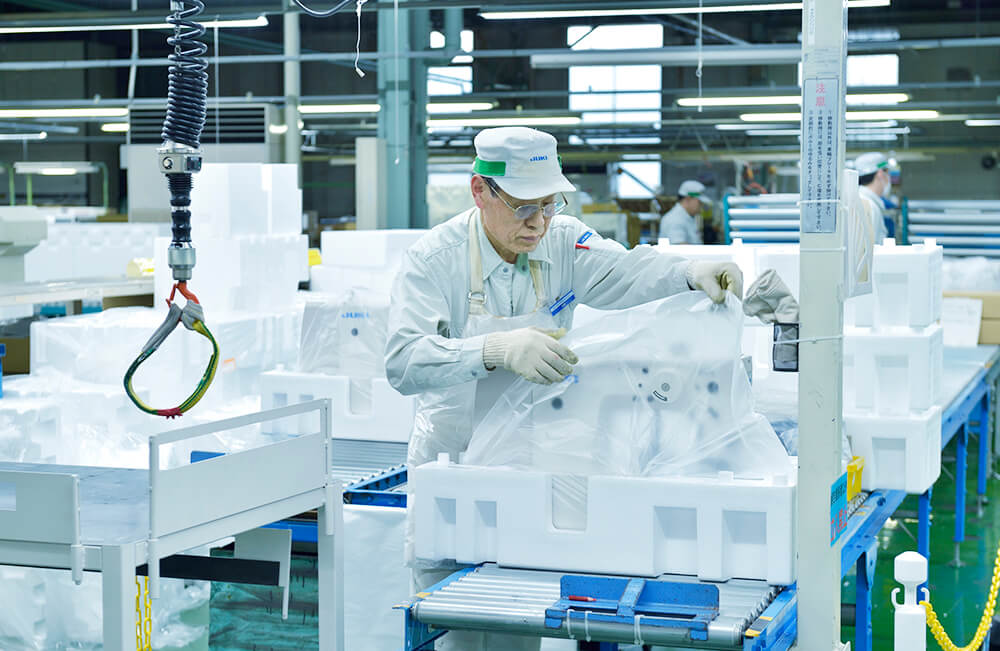
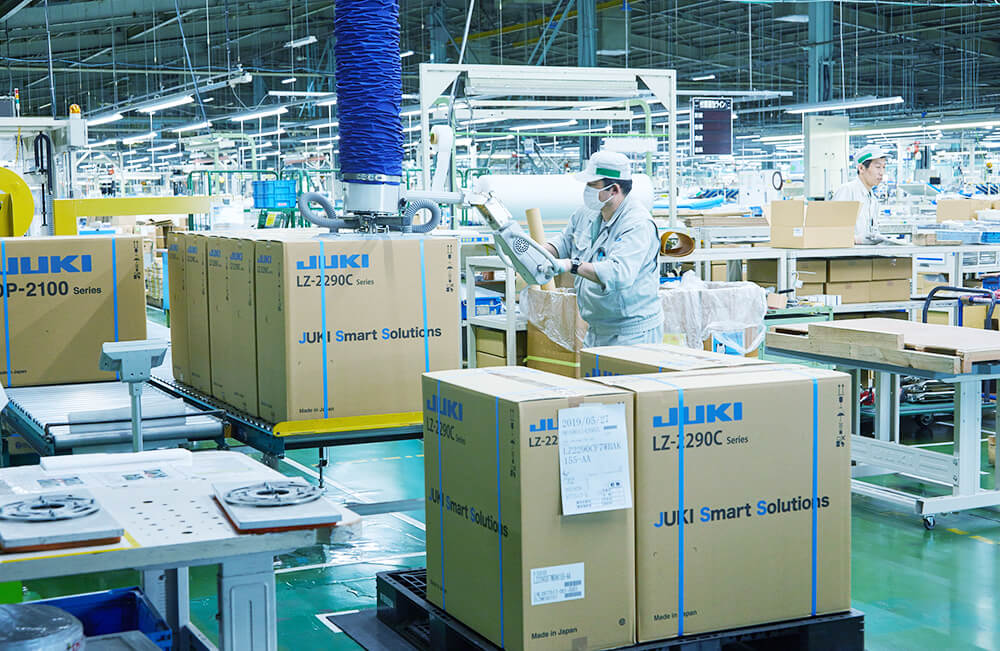
Packing and shipping
We carefully pack the products one by one and ship them to customers both at home and abroad.








